Transmission Line Electrical Characteristics: Efficient Power Flow Explained
Explore resistance, inductance, capacitance, and conductance of transmission lines key factors for efficient, stable power delivery.
ELECTRICAL CHARACTERISTICS OF TRANSMISSION LINES & BASIC CLASSIFICATION OF LINE LENGTH:
Electrical power is transferred from generating stations to consumers through overhead lines and cables.
Overhead lines are used for long distances in open country and rural areas, whereas cables are used for underground transmission in urban areas and for underwater crossings. For the same rating, cables are 10 to 15 times more expensive than overhead lines and they are therefore only used in special situations where overhead lines cannot be used: the distance in applications is short.
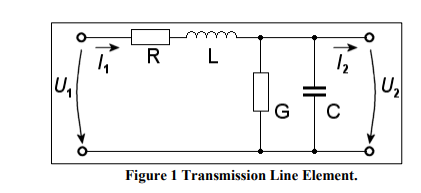
Since all cables are subject to the same impacts despite their differences, an equivalent circuit diagram for one cable may be drawn, as illustrated in Figure 1. The transmission line is affected by an ohmic series resistor R, a line inductance L, an insulation value G, and a line capacitance C.
(a) Overhead lines
A transmission line is characterized by four parameters: series resistance R due to the conductor resistivity, shunt conductance G due to leakage currents between the phases and ground, series inductance L due to the magnetic field surrounding the conductors, and shunt capacitance C due to the electric field between conductors.
Series Resistance (R)
The resistances of lines accounting for stranding and skin effect are determined from the manufacturer's tables.
With the formula the resistance can be described as:
Categories: : Load flow
Not sure how to get started with design engineering? want a free consulting call?
We’ve got you covered!
Fill out the form to get personalized guidance on how to:
✱ Transform your career in electrical engineering
✱ Discover the best tools and software to learn
✱ Identify the next steps to take toward design engineering
Start your journey today!
 Power Projects
Power Projects